
Note: The Maikomidaira Geosite is located within a remote, poorly accessible region of rugged, dangerous topography.
Until further preparation can be made, access to Maikomidaira is restricted to specially-planned guided tours.
Road & Geosite Conditions
Partially Accessible
- Number
- Area
- 1. Ichiburi Geosite
- 2. Oyashirazu Geosite
- 3. Omi Coast Geosite
- 4. Omigawa Jade Gorge Geosite
- 5. Imai Geosite
- 6. Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line and Salt Trail(North) Geosite
- 7. Maikomidaira Geosite
- 8. Hashidate Gold Mine Geosite
- 9. Kotakigawa Jade Gorge Geosite
- 10. Tsugami Shindo Geosite
- 11. Himekawa Gorge Via Oito Line Geosite
- 12. Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line and Salt Trail(South) Geosite
- 13. Himekawa Gorge Geosite
- 14. Renge Geosite
- 15. Itoigawa Coast Geosite
- 16. Miyama Park and Museums Geosite
- 17. Tsukimizunoike Geosite
- 18. Umidani Gorge Geosite
- 19. Amakazariyama Geosite
- 20. Yakeyama Geosite
- 21. Benten-iwa Geosite
- 22. Shindosan Geosite
- 23. Gongendake Geosite
- 24. Tsutsuishi Hamatokuai Geosite
- Jade
- 1. Ichiburi Geosite
- 2. Oyashirazu Geosite
- 3. Omi Coast Geosite
- 4. Omigawa Jade Gorge Geosite
- 9. Kotakigawa Jade Gorge Geosite
- 15. Itoigawa Coast Geosite
- 16. Miyama Park and Museums Geosite
- Fossa Magna
- 5. Imai Geosite
- Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line and Salt Trail(North) Geosite
- 11. Himekawa Gorge Via Oito Line Geosite
- 12. Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line and Salt Trail(South) Geosite
- 13. Himekawa Gorge Geosite
- 17. Tsukimizunoike Geosite
- 21. Benten-iwa Geosite
- 22. Shindosan Geosite
- 24. Tsutsuishi Hamatokuai Geosite
- Mountainous areas
- 7. Maikomidaira Geosite
- 8. Hashidate Gold Mine Geosite
- 10. Tsugami Shindo
- 14. Renge Geosite
- 18. Umidani Gorge Geosite
- 19. Amakazariyama Geosite
- 20. Yakeyama Geosite
- 23. Gongendake Geosite
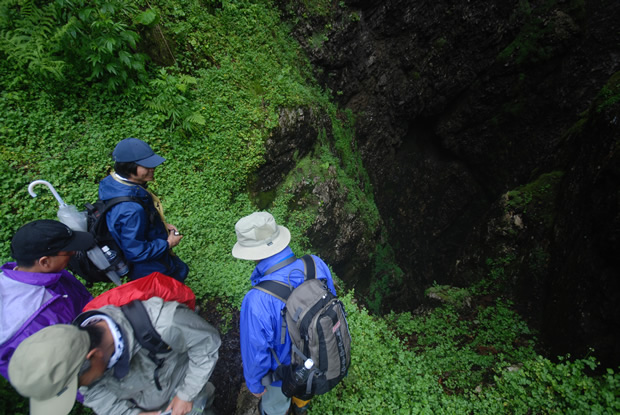

Maikomidaira is a large polje. a type of basin that is characteristic of karst topography. Situated on the southern side of Mt. Kurohimeyama, a 1,222 meter limestone mountain, the entire region is blanketed with dolines, ponors, vertical caves, and other features of karst topography.
Karst topography is a type of landform created when large areas of soluble rock (such as limestone) dissolve, leaving behind unique stone formations and caves.
As a result of the protuberance of the surrounding limestone areas, several vertical caves measuring hundreds of meters deep have taken form in the area. Including Byakuren Cave (Deepest in Japan at 513m) and Senri Cave (Second deepest at 405m), the four deepest caves in Japan are found here in Maikomidaira. Water which collects in Maikomidaira travels approximately 3.5km underground to Fukugakuchi Limestone Cave where it is expelled into what becomes the Toumigawa River, finally emptying into the Sea of Japan.
With heavy snowfall common for the region, snow often collects in the dolines at Maikomidaira, where they often remain throughout summer, creating an environment not unlike that of the glacial periods. Entering into the bottom of the sink holes, various alpine flora appear. These plants are usually not found below elevations of 2,500m. Partially owing to the dangerous nature of the topography here, entrance to Maikomidaira is restricted to those who have obtained special permission.
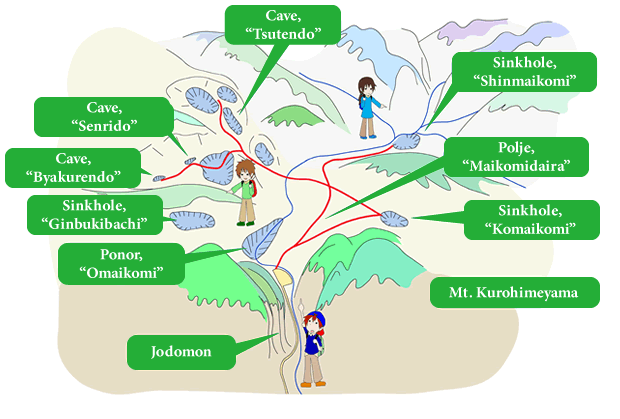

Senri Cave
(vertical cave, depth 405m)

Byakuren Cave
(vertical cave, depth 513m)

Maikomidaira

Mt. Kurohimeyama (1,222m)
Route to Maikomidaira Geosite
Destination:
